+86 13630122007
+86 13630122007 CNC Machine Tools: Popular Science Knowledge
Core Definition and Advantages
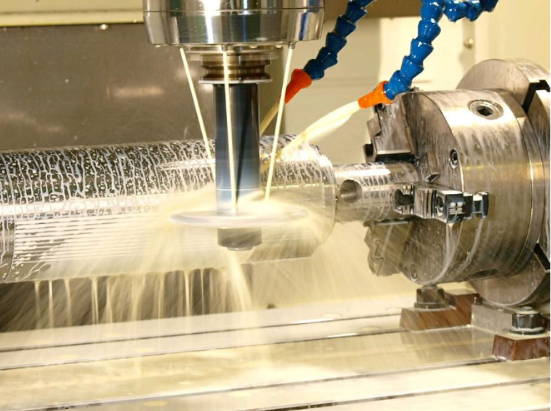
• Definition: Digital instructions input via a computer control the movement of the machine's spindle and Cutting Tools, enabling processes such as cutting and grinding of parts.
• Core advantages: High machining precision (errors controllable at the micrometer level), high production efficiency (no need for repeated manual adjustments), ability to process complex shapes (e.g., curved surfaces, special-shaped parts), and high automation (reducing manual intervention). Main Classifications
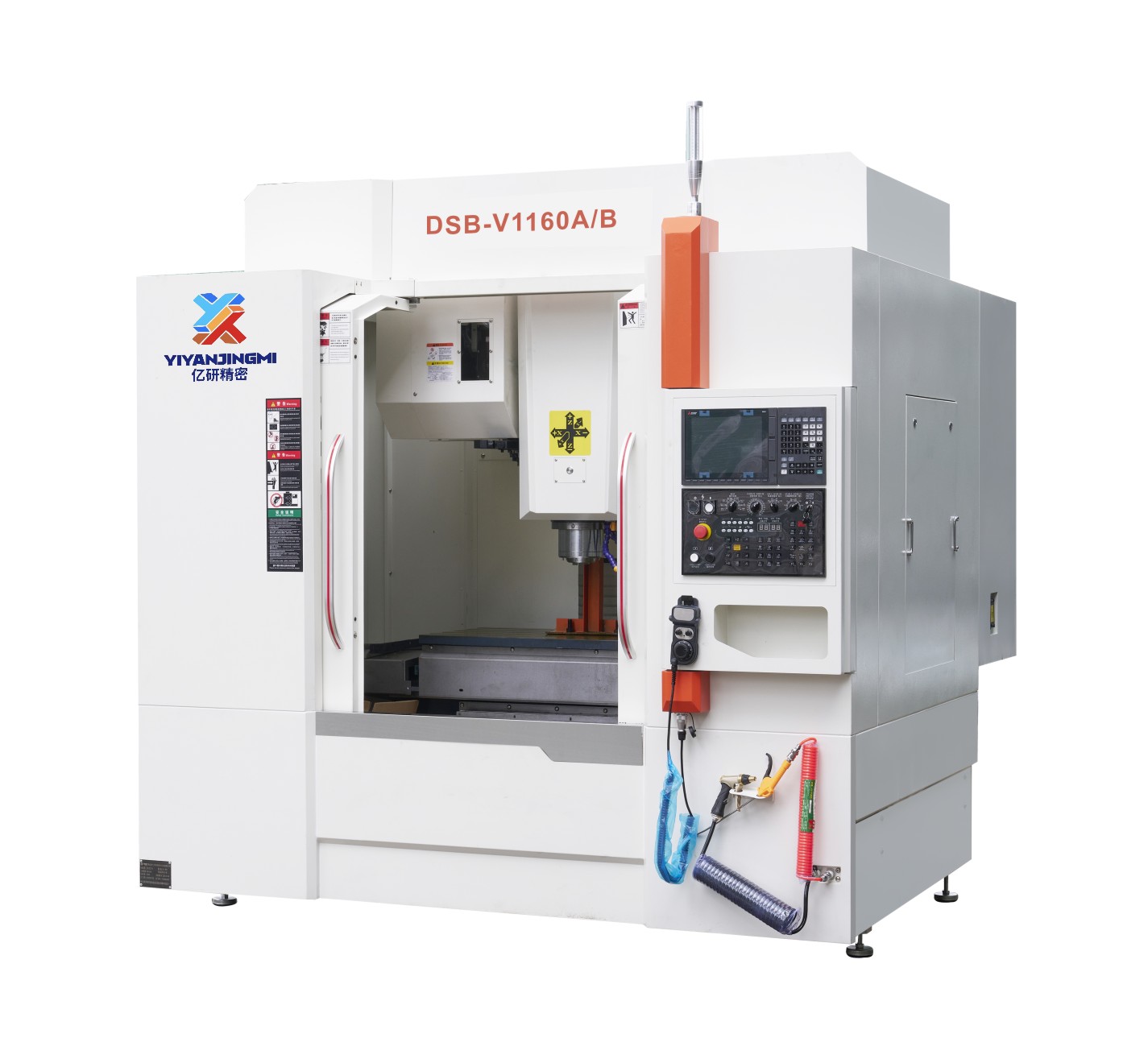
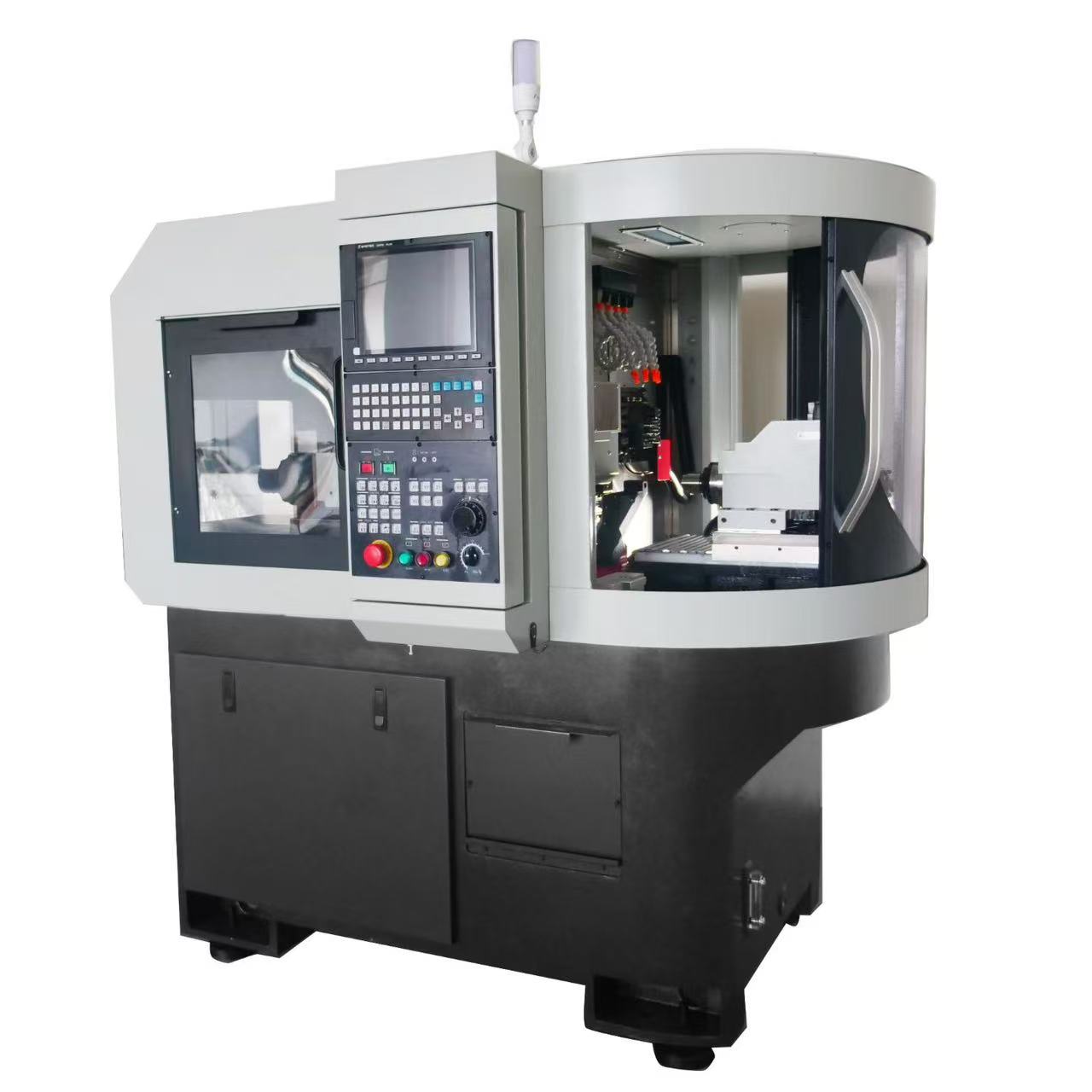
• By processing method: CNC lathes (for shaft and disk parts), CNC milling machines (for planes, grooves, curved surfaces), machining centers (integrating milling, drilling, boring and other functions), CNC grinding machines (high-precision grinding) and so on.
• By control method: Point-to-point control (only controlling tool positioning), linear control (controlling linear motion machining), contour control (controlling complex curve/surface machining).
Key Components
• Control system: The core is the CNC system (e.g., FANUC, Siemens), which receives and parses programs and issues control commands.
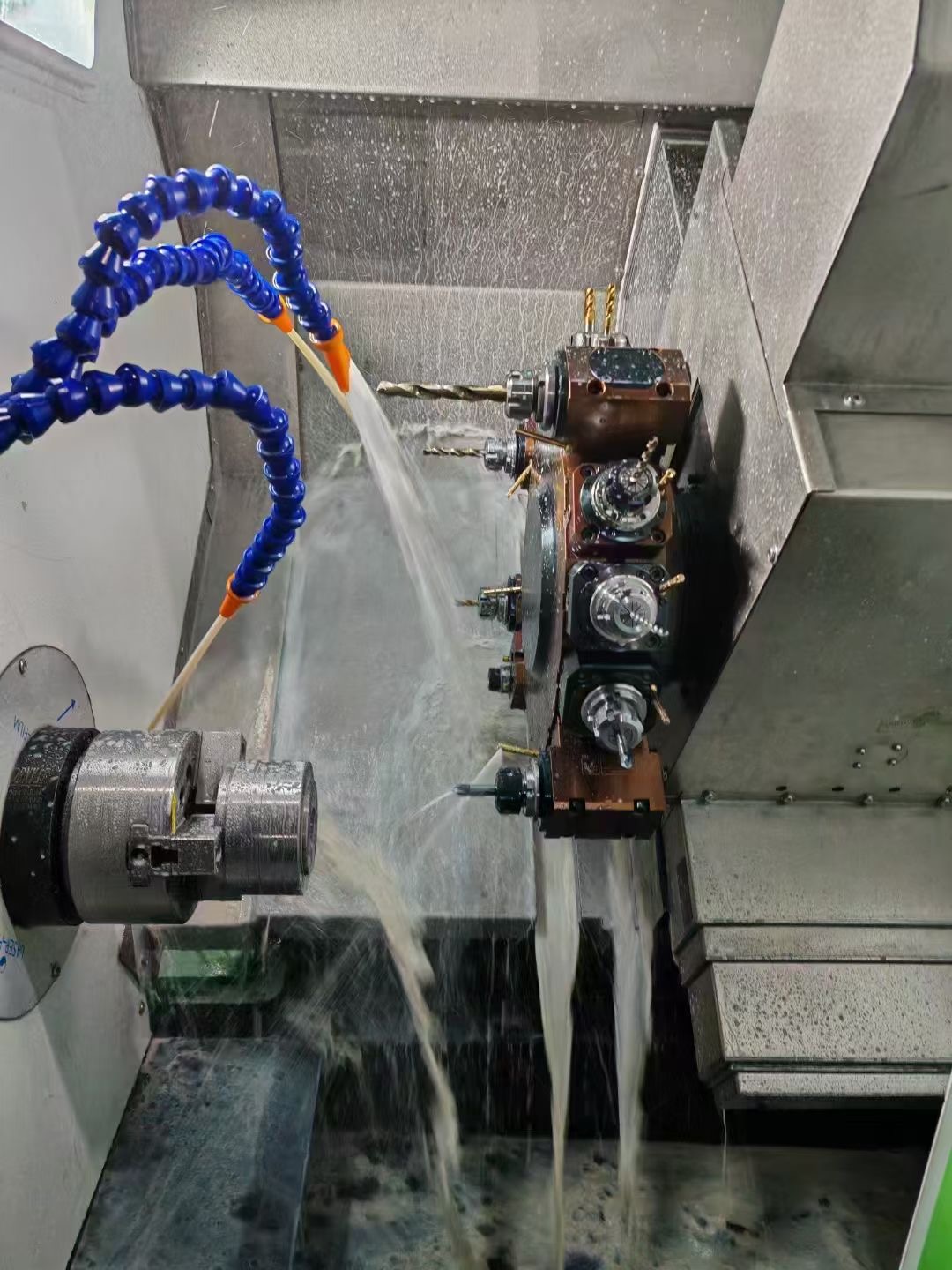
• Executive mechanism: Includes the spindle (driving the workpiece/tool rotation), feed system (controlling tool/workpiece movement), and Tool Magazine (storing multiple tools for automatic tool change).
• Auxiliary system: Covers cooling, lubrication, chip removal, and hydraulic/pneumatic systems to ensure stable machining operation.
Application Fields
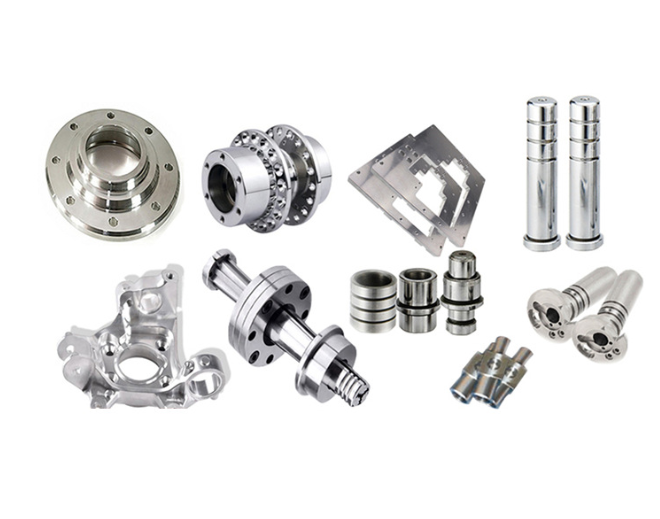
• Machinery manufacturing: Processing of auto parts, machine tool accessories, and general mechanical components.
• Aerospace: Manufacturing of high-precision parts such as engine blades and aircraft structural components.
• Electronic and electrical appliances: Processing of precision parts for products like mobile phones and computers.
• Medical equipment: Processing of high-precision metal components in medical devices.